# Dashboard Design
A dashboard is typically a visualization interface in a system used to provide an overview of key data and metrics. It usually presents information in the form of charts, graphics, numbers, etc., aimed at helping users intuitively monitor and understand the system's status, performance, or other key indicators.
This system supports customizing dashboards through customization to display various charts, links, text descriptions, etc.
# Target Audience
The target audience for this document includes: developers and implementers of this system, or advanced users interested in customizing dashboards.
# Operation Overview
# Creating a Dashboard
Users with dashboard creation permissions will see a button to create a new dashboard on the homepage after logging into the system, as shown below:
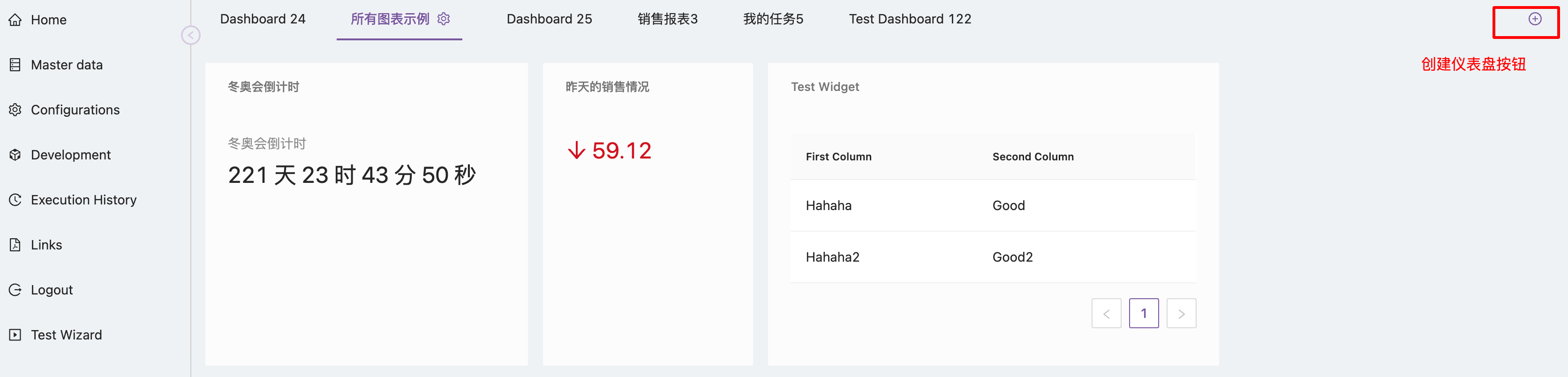
Clicking this button will bring up the dashboard creation form as follows:
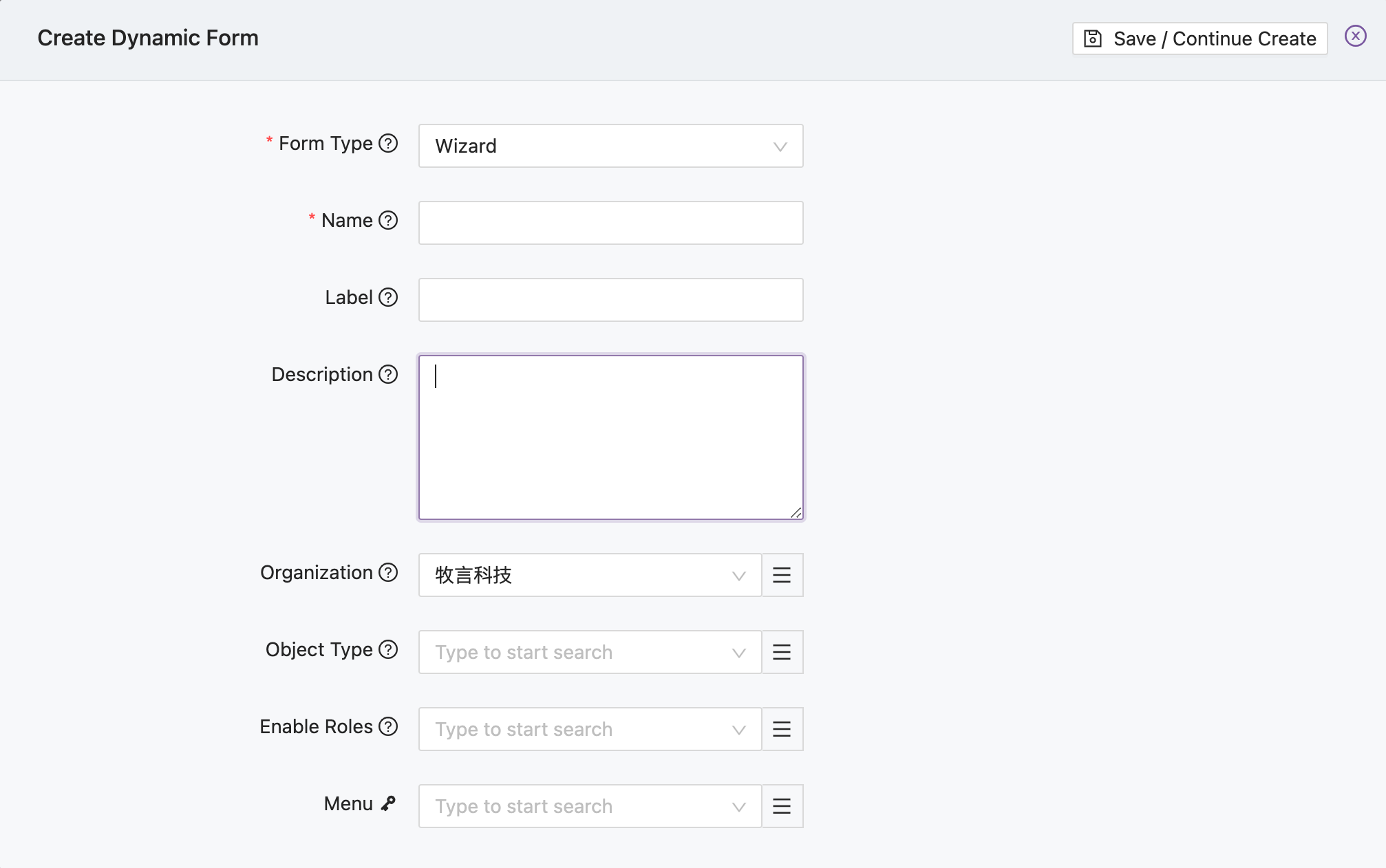
The key fields are described as follows:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
Form Type | Set to Dashboard when creating a dashboard |
Name | The name of the dashboard, cannot be modified after setting |
Label | The display name of the dashboard in the interface |
Organization | The organization to which the dashboard belongs |
Enable Role | List of user roles that can view this dashboard. If the user also has dashboard editing permissions, they can also edit the dashboard |
TIP
Whether a user has permissions to create, edit, or delete a Dashboard is determined by whether the user has corresponding permissions for the DynamicForm Domain object.
# Dashboard Editing and Other Related Operations
- Switch to the dashboard to be modified, and click the gear icon after the dashboard display label to bring up the dashboard operation menu, which includes the following related functions:
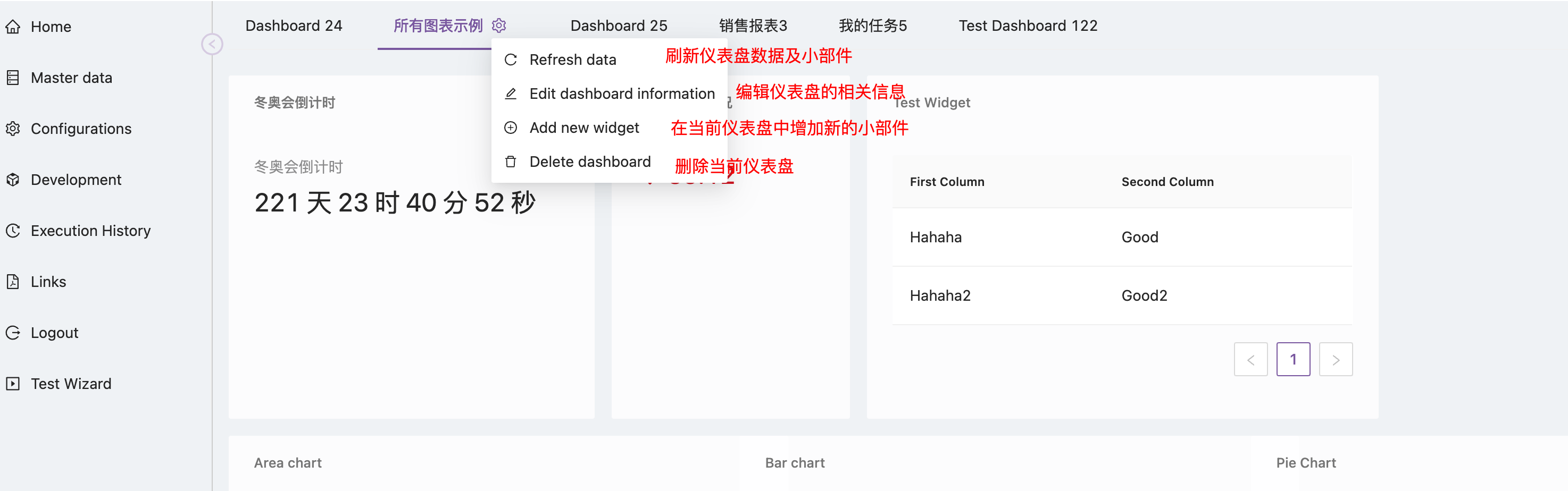
The process of editing a dashboard is similar to creating one, so it won't be repeated here.
# Adding a Widget
In the dashboard operation menu mentioned above, clicking "Add new widget" will add a new widget to the current dashboard. The form for adding a new widget is shown below:
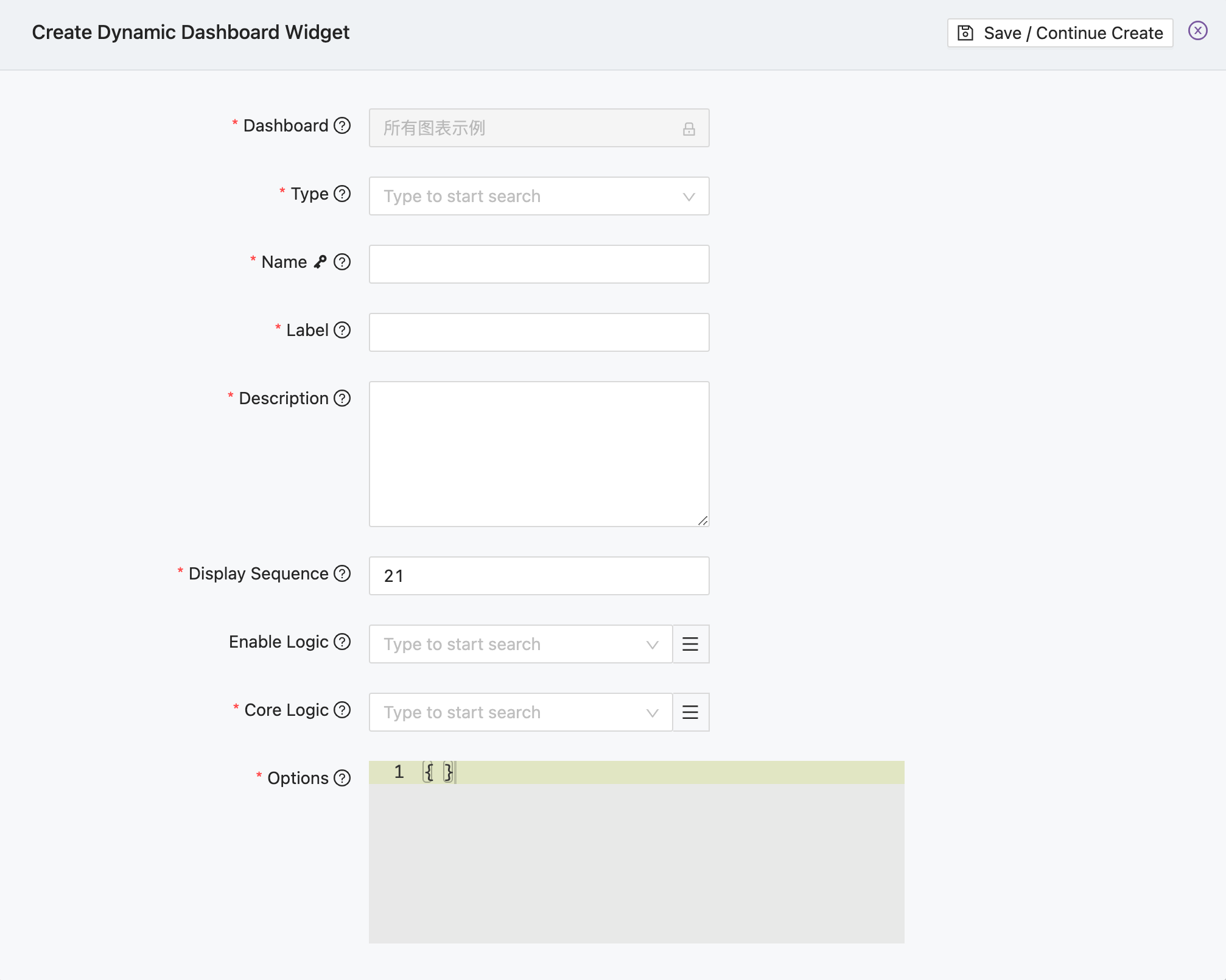
The key fields are described as follows:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
Dashboard | The dashboard to which this widget belongs |
Type | The type of this widget, which determines how it will be rendered in the frontend |
Name | The name of the widget, a unique identifier that cannot be modified after creation |
Label | The display name of the widget |
Display Sequence | The display order of the widget, widgets with smaller display sequence values are displayed first |
Enable Logic | The dynamic logic for whether the widget is displayed. If the result is false, the widget will be hidden |
Core Logic | The core logic for data preparation and display configuration of the widget |
Options | A JSON string that stores the display configuration of the widget |
- For detailed description of the
Optionsfield of the widget, please refer to the Widget Options Setting section - For detailed description of the widget's enable logic and core logic, see the Widget-related Dynamic Logic section
# Modifying and Deleting Widgets
When you hover over a widget, a gear icon will appear in the upper right corner of the widget. Clicking this gear icon will bring up an operation menu as shown below:
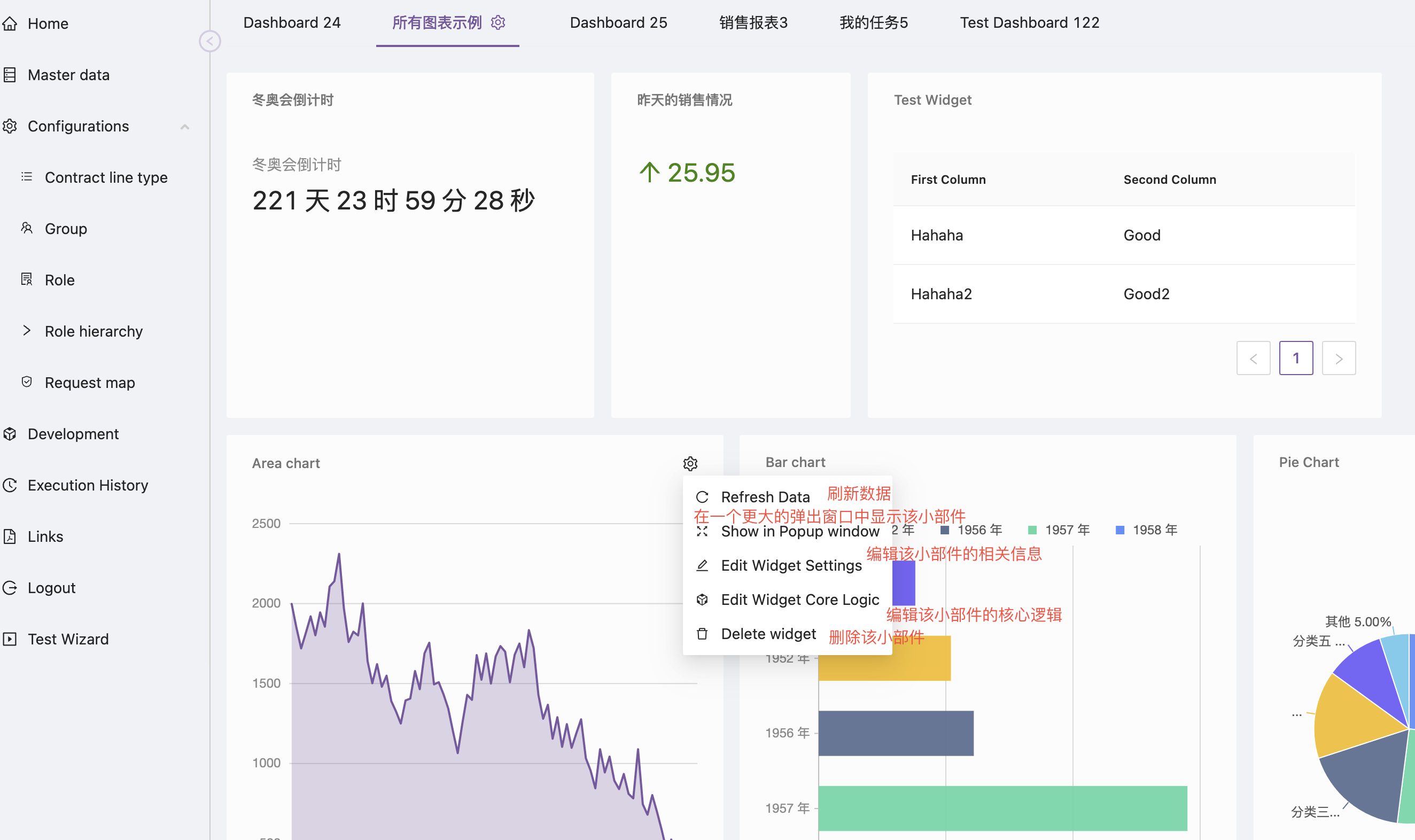
If the current user has permission to edit the widget, the following related operation menu items will appear:
- Refresh data: Refresh the data
- Show in popup window: Display the content of the widget in a larger popup window
- Edit Widget settings: Edit the related settings of the Widget
- Edit widget core logic: Edit the core logic of the widget. The core logic of the widget is a dynamic logic object used to return the data and configuration information needed to render the widget to the frontend
# Widget Display Width Setting and Line Break
When laying out widgets, the system divides all displayable width horizontally into 24 grids. Each widget can be set to a display width from 1 to 24. The system will sort the widgets based on the display sequence and calculate how many widgets can be displayed in each row based on the width setting of each widget, ensuring that the total width of all widgets in each row does not exceed 24. If the remaining grid width in a row is not enough to accommodate the next widget to be displayed, that widget will be moved to the next row for display.
The display width is saved in the Options field and specified through the
following JSON data:
// "col": 8 indicates that the display width of this widget occupies 8 horizontal widths, i.e., 1/3 of the total width
{"position": {"col": 8}}
2
TIP
If the width of the widget is not specified in Options, the default width of
the widget is 12, occupying 1/2 of a row.
# Widget Display Height
All Widgets displayed in the same row have the same height.
# Widget Options Setting
The Options in the Widget definition is a JSON string that defines the display
configuration of the widget, including width and other configurations that only
apply to specific widget types.
In addition, the configuration defined under the config key in the Options
field will be passed to the rendering React component without any modification
when rendering the widget in the frontend. In the following Options setting,
the JSON object {"xField": "year", "yField": "value", "tooltip":{"showMarkers": true}}
will be passed to the rendering React component as is.
{"config": {"xField": "year", "yField": "value", "tooltip": {"showMarkers": true}}, "position": {"col": 8}}
# Widget-related Dynamic Logic
# Enable Logic
Whether a Widget is displayed is controlled by the widget's enable logic, while the related configuration and data for display,
The enable logic of a Widget is a Dynamic Logic object with Logic Type "Dashboard widget enable logic"
# Injected Variables
When the frontend retrieves the widget list of a Dashboard, it will first call the enable logic dynamic logic defined in each widget definition and perform the calculation . If the calculation result is false, that widget will not be returned. The list of variables injected at runtime is as follows:
# Return Result
The customized code needs to return a Map<String, Boolean> object, which
should contain an element with key result, as shown in the example below:
// 表示该 action 或 task 或 widget 是否启用
// Indicates whether this action or task or widget is enabled
[result: true | false]2
TIP
If the enable logic field in the widget definition is empty, it means that the widget is displayed by default
# Core Logic
The system generates the specific data to be displayed and related display attributes through the widget's core logic, and passes them to the frontend.
# Injected Variables
The injected variables when the Widget core logic runs are shown in the table below:
# Return Result
The result returned by running the Widget core logic is an object of type
Map<String, Object>. The system will directly pass this Map object to the
frontend. When rendering, the frontend will directly convert this Map object
into a JSON object, and merge it with the default properties defined in the
Widget's frontend rendering component and the JSON object with key config in
the Widget definition's Options. After merging, the merged result is used as
the property set of the Widget's frontend rendering component.
For example:
- The value of the
Optionsfield in the Widget definition is as follows, wherexFielddefines the x-axis of the chart asyear, andyFielddefines the y-axis asvalue
{"config": {"xField": "year", "yField": "value", "position": {"col": 8}}
- The value of the Map returned in the Widget core logic is as follows
def data = [
[x: 1, y: 2],
[x: 3, y: 4]
]
def result = [
data: data,
legend: [
custom: true,
position: 'bottom',
]
]
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Then the final properties passed to the React rendering component are the merge of the above two sources.
Among them, the xField and yField properties come from the Options field in
the widget definition, and the data and legend properties come from the return
value of the Widget core logic
{
"xField": "year",
"yField": "value",
"data": [
{"x": 1, "y": 2},
{"x": 3, "y": 4}
],
"legend": {
"custom": true,
"position": "bottom"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# Widget Type Details
# Supported Widget Type List
The following lists the widget types currently supported by the system and their brief descriptions
| Type | Description | Corresponding Internal Rendering Component |
|---|---|---|
| MARKDOWN | A markdown content | Uses react-markdown (opens new window) for rendering |
| HTML | An HTML content | Displays an HTML content |
| COUNTDOWN | A countdown widget | Statistic (opens new window) |
| STATISTIC | A single value statistic | Statistic (opens new window) |
| DATATABLE | Displays a table | Table (opens new window) |
| PIE_CHART | Pie chart | Pie chart (opens new window) |
| LINE_CHART | Line chart | Line chart (opens new window) |
| COLUMN_CHART | Column chart | Column chart (opens new window) |
| GAUGE_CHART | Gauge chart | Gauge chart (opens new window) |
| LIQUID_CHART | Liquid chart | Liquid chart (opens new window) |
| BULLET_CHART | Bullet chart | Bullet chart (opens new window) |
| AREA_CHART | Area chart | Area chart (opens new window) |
| BAR_CHART | Bar chart | Bar chart (opens new window) |
| PROGRESS_CHART | Mini progress bar | Progress chart (opens new window) |
| RING_PROGRESS_CHART | Ring progress chart | Ring progress chart (opens new window) |
| TINY_AREA_CHART | Tiny area chart | Tiny area chart (opens new window) |
| TINY_LINE_CHART | Tiny line chart | Tiny line chart (opens new window) |
| TINY_COLUMN_CHART | Tiny column chart | Tiny column chart (opens new window) |
| BI_DIRECTION_BAR | Bidirectional bar chart | Bidirectional bar chart (opens new window) |
| HISTOGRAM | Histogram | Histogram chart (opens new window) |
Related widget types have specific settings or usage notes, detailed as follows
# Non-Chart Widget Property Structure
# Markdown and Html Widgets
Below is the structure of the core logic return value for markdown and html type widgets
// A Map object containing a key 'data' with the display text as its value
[ data: "Markdown text" ]
2
3
4
:::
You can set the overall style of the widget in the Html widget's options through
the config field, for example
{
"config": {
"style": {
"color": "red",
"fontSize": "32px",
"textAlign": "center"
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
You can also set the overall style of the widget in the widget's core logic
return value through the style field, for example
return [
data: "Hello World",
style: [
// Optional CSS styles
fontSize: "12px"
]
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TIP
Markdown widget supports gfm standard (opens new window) through remark-gfm (opens new window), which includes some advanced format controls such as tables, lists, TODOs, etc.
# Countdown Widget
Below is an example of the core logic return value structure for countdown type widgets
Date d = new Date()
d.setYear(2022 - 1900);
d.setMonth(1)
d.setDate(4);
return [
// Title is the title of the countdown displayed on the interface
title: 'Winter Olympics Countdown',
// Value is the target time of the countdown, the system will automatically generate the countdown display based on the current time
value: d.getTime()
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Data Table Widget
Below is an example of the core logic return value structure for data table type widgets
return [
// Contains an array with key 'data', and value being the data to be displayed
// Each element of the array is a Map type structure
// The structure below will be rendered into a table with two columns in the frontend
// The column titles are First Column and Second Column respectively
data: [
[
"FirstColumn": "Hahaha",
"SecondColumn": "Good"
], [
"FirstColumn": "Hahaha2",
"SecondColumn": "Good2"
]
]
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Statistic Widget
Below is an example of the core logic return value structure for Statistic type widgets
return [
// title is the title displayed on the interface
title: "Yesterday's Sales",
// value is the value displayed on the interface
value: 50
// direction can be 'up' or 'down', determining the color and direction of the arrow displayed on the interface
direction: "up" | "down"
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
The widget display effect and the correspondence between each part and the parameters passed from the backend are shown in the figure below

# Chart Type Widgets
All dashboard charts are rendered using the antd chart (opens new window) chart library, but currently only a subset of chart types are supported. Please refer to the above table for the specific support list.
When a chart Widget is rendered, the part with key config in the Options
field of the Widget definition will be merged with the top-level keys in the Map
returned by the Core Logic, and the merged result will be directly passed as
parameters to the antd chart rendering component.
Compatibility Note
The current widget rendering does not support JavaScript callback function type rendering properties.
# Chart Axis Settings
For chart types that include axes, axis settings need to be included in the
Options of the widget or in the return value of the core logic, otherwise the
chart may appear empty or display incorrectly.
- Setting in the
Optionsfield
// Set x-axis to year, y-axis to value
{"config": {"xField": "year", "yField": "value", "position": {"col": 8}}
2
- Directly return in core logic
return [
xField: "Time",
yField: "Sales"
data: [...]
]
2
3
4
5
List of charts where xField and yField are required properties:
- Line chart
- Area chart
- Column chart
- Bar chart
List of charts where xField is an optional property:
- Bullet chart
# List of value properties for charts
According to the Antd chart API, the property names for displaying data in charts may vary. The following table lists the data property names for various charts for reference. Please refer to the Antd chart documentation for specific property value formats.
| Chart Type | Data Property Name |
|---|---|
| Line chart | data |
| Area chart | data |
| Column chart | data |
| Bar chart | data |
| Pie chart | data |
| Gauge | percent |
| Liquid | percent |
| Progress chart | percent |
| Bullet | data |
| Ring progress chart | percent |
| Tiny area chart | data |
| Tiny line chart | data |
| Tiny column chart | data |
| Bi-direction bar | data |
| Histogram | data |
TIP
The value property in the core logic return result is required, otherwise the chart will not be displayed.
Compatibility Note
The current version of Antd chart is 1.0.11. Please note that in future
versions, the Antd chart API may change. If the above properties become invalid,
please refer to the latest API documentation for each chart.
# Notes
The following lists the considerations and best practices for implementing dashboards.
# Priority of Widget Display Properties
When rendering widget controls, the system merges the widget's core logic,
Options field, and default properties defined in the front-end rendering
control as the final control rendering properties. The following lists the
priority of properties from these three sources. For properties with the same
name, values from higher priority sources will override values from lower
priority sources.
* Highest: Display properties returned in the widget's core logic
* Second: Display properties defined in the widget's Options field
* Lowest: Default display properties of each widget's React control
# Best Practices
# Line breaks in Markdown widget
If you need to add line breaks in the rendered result, you can add two spaces at the end of the line. The final rendered effect will include a line break.
# Minimum Widget Width
If the widget width is set to less than 4 (Widget Options width set to 1, 2,
or 3 {"position": {"col": 1 | 2 | 3}}), there is a chance that the widget may
overlap with the following widget. Therefore, it is recommended to set the
minimum widget width to 4 or above (occupying 1/6 or more of the total width)
when designing widget layout.
# Special Note on Options Field Format
The Options field in the Widget definition is saved as a jsonb type field in
the database. As required by PostgreSQL, all strings in this JSON string must be
enclosed in double quotes, not single quotes. For example, {"position": {"col": 8}} cannot be written as {'position': {'col': 8}}, otherwise saving
to the database will fail.
# Related Implementation Background Development
The following lists some framework implementation details that may be helpful for creating dashboards and troubleshooting issues.
- In the system, a dashboard is a type of form (Form) of type Dashboard, which
is the same as object CRUD and wizard-defined forms, all stored in the
dynamic_formdatabase table. - The APIs for dashboard metadata retrieval, rendering, data retrieval, etc.,
all start with
/dashboard/. For details, please refer to the Swagger page in the system.